EMD-API - Global Atlas Services
Introduction

The Global Atlas Services is one of several services available from the EMD-API. This service created in order to provide an interface (REST/OpenAPI standard) to atlas-data on wind-resources, siting-data (such as site flow characteristics), geospatial-predictors and elevations. The service delviers a unified interface to a wide range of atlas data, and has the following key features:
- Instant data delivery: All datasets within the EMDAPI are ready processed and requests are served within seconds or minutes
- Hundreds of atlas parameters for renewable energy: EMDAPI provides access to hundreds of parameters on winds, siting, elevations and other geospatial parameters used within renewable energy
- Unified interface: The unified interface which allows for integration to internal processes and tools
- Trusted datasets: EMDAPI builds upon the trusted data-bases and data-sources is also used through the online-data services in windPRO, some for more than a decade.
- Built on open standards: EMDAPI is a REST based service that implements the OpenAPI standard].
- Available from any development tool: Access to the climate databases is available from your preferred development platform - C#, R, python, html, java, php, scala and swift. Just use the OpenAPI tools to generate the client software for your preferred platform.
Access
The Global Atlas Service API is currently (June 2021) in beta-release. To see more documentation and to access the data-services, please visit the API through the following URL's:
- EMD-API Overview (Wiki) - here.
- EMD-API Main Page (API) - here.
- EMD-API Global Atlas Service UI (API) - here.
Any technical questions on our global atlas service can be addressed to our Senior Technical Specialist - Morten Lybech Thøgersen: mlt@emd.dk.
Usage Constraints and Restrictions
Each API-access-token provides a full, virtually unrestricted access to the atlas datasets. So, even though data access is ‘flat rate’ and without any limitations on the number downloads or number of climate-variables – it is not permitted to do parallel downloads from the same API-token. This is to ensure enough bandwith and a good experience for all API users. This restriction is - from november 2022 - enforced through "rate limiting" - allowing up to 20 API-data-requests per running 10-minute interval. If you exceed this limit, a "HTTP ERROR 429: TOO MANY REQUESTS" is shown until below the limit again. Only the following endpoints are part of the rate-limiting procedure:
- /download_area/
- /download_point/
- /order_area/
- /order_point/
Our recommended approach for API-processing and download is as from the pesudo-code below:
prepare list of nodes to download (from "coverage checks") loop through list: request to download point wait at minuimum 30 seconds for api-server to finalize data-processing (until status = "success") download node from provided url
Data Model - Global Atlas Service
The EMD global-atlas-services is documented in a REST based API using the OpenAPI Specification. You can view the interfaces and download the interfaces as json or yaml, here. The service provides the following functionality:
- Datasets: List of available datasets with their ID’s, available parameters, descriptions and documentation links (URL's).
- Coverage: Check if a particular dataset has coverage at a certain location.
- Download: Request to download data for a certain location. Typically, the interface provides the possiblity to download the data in various formats.
Python - Installation
The simplest way to use the global atlas service within python is to install the client software in a virtual environment. If you are using CONDA or MINICONDA, we recommend that you create a new virtual environment and use a recent 3.x version of python. When the virtual environment is created, then activate the environment.
Open your Anaconda Prompt. Copy-paste the following lines:
conda create -n emdapiclient python=3.8.5 conda activate emdapiclient
Install the required packages needed in order to do data-science and use the examples provided within the jupyter notebooks. We have have validated this setup using specific package versions (used in the commands below).
In the Anaconda Prompt, copy-paste the following lines, one by one:
conda install -c conda-forge pandas=1.1.0 numpy=1.19.1 conda install -c conda-forge matplotlib=3.3.1 basemap=1.2.2 basemap-data-hires=1.2.2 conda install -c conda-forge jupyter=1.0.0 ipykernel=5.3.4 conda install -c conda-forge tabulate=0.8.7 shapely=1.7.1 pyproj=3.0.0 conda install -c conda-forge python-wget pip install tilemapbase
Download the zipped-file holding the OpenAPI python client for the global atlas data service. Unpack the file and install it within your virtual environment:
In the Anaconda Prompt: Move to the folder, where you have unpacked the zipped file. Copy-paste the following line:
python setup.py install
Python and Jupyter Notebook Examples for Demonstration and Test
In order to test your setup and learn how-to use the EMDAPI Global Altas Service, we suggest that you download our python examples (one Jupyter notebook with 'point' analysis and a python script wiht 'area' downloads (as siteres and netcdf formats) - here.
Unpack the zip file and run the command below in your terminal or command-shell.
If Jupyter prompts for you to select another Python-kernel, then select the emdapiclient kernel (may also be selected directly from the 'Kernel' drop-down menu).
Make sure that the new emdapi virtual environment (python-kernel) is available to be used with Jupyter Notebook environment:
python -m ipykernel install --user --name=emdapiclient
In the Anaconda Prompt: Move to the folder, where you have saved the Jupyter Notebook examples. Copy paste the following line to open Jupyter Notebook from where you can open the examples.
jupyter notebook
Within the internet-browser (and Jupyter user-interface), run select the Jupyter Notebook file (*.ipynb).
Then work your way through the example provided:
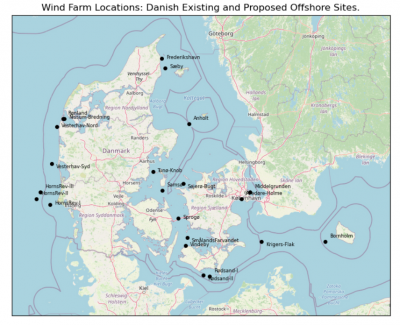
- emdapi_atlasservice_offshore-dk.ipynb Demonstration of login to the system and requesting atlas data for the offshore sites in the image to the right.
- emdapi_atlas_areas.py': Demonstration of atlas-area download on 5 sites around the globe.
Client Software - Other Languages and Tools
REST and OpenAPI is easily consumed from a lot of software tools. It is perfectly possible that your preferred language is supported. OpenAPI works well with languages such as - but not limited to - C#, R, python, java, php, scala and swift. Just download the YAML or JSON service description and use the Swagger Editor or OpenAPI Generator to generate the client libraries for your preferred software. Then you are ready to integrate towards your preferred systems and workflows.
To generate the client libries yourself - one possible process is to: